Ulcerative Colitis
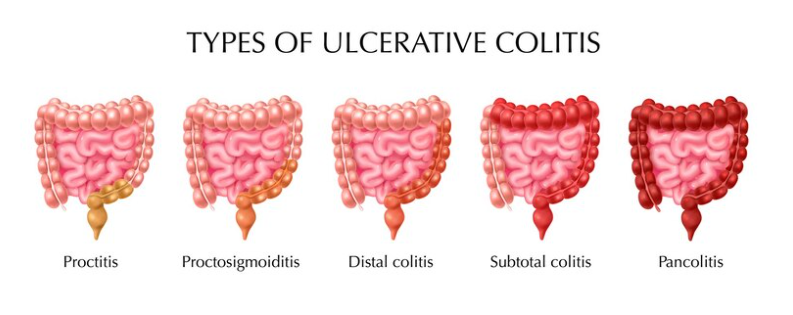
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease characterized by inflammation and ulcers in the colon and rectum. It follows a relapsing-remitting course, with periods of flare-ups and remission. Here are key aspects of ulcerative colitis:
Symptoms:
- Rectal bleeding
- Diarrhea, often with blood
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Urgency to have bowel movements
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
Diagnosis:
- Colonoscopy to visualize the colon and rectum
- Blood tests to assess inflammation and nutritional status
- Imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs
Causes:
- The exact cause is unknown, but it involves a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and immune factors.
- Abnormal immune response leads to inflammation in the colon.
Treatment:
- Medications such as aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologics to control inflammation.
- Nutritional therapy, including supplements to address deficiencies.
- Surgery in severe cases, where removing the colon may be necessary.
Management:
- Lifestyle modifications, including a well-balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Stress management.
- Monitoring for potential complications like colon cancer and osteoporosis.
Challenges:
- Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition with no cure.
- It can significantly impact the patient’s daily life and quality of life.
- Flare-ups and remission are unpredictable.
Individual Variability:
- The severity and extent of inflammation can vary widely among individuals.
- Treatment plans are tailored to each patient’s specific symptoms and needs.
Long-term Outlook:
- With proper management, many individuals with ulcerative colitis can achieve and maintain remission.
- Regular monitoring, adherence to treatment plans, and adjustments when necessary are crucial for long-term control of the disease.

